Possibilities and challenges of using logic programming for representation, search and analysis of information in the Internet are considered. The mathematical problem of providing strict declarative semantics of logic programs executing in conditions of changing the structure and information of the Net is considered. Approach based on developed logic object-oriented programming is proposed.
Introduction
The idea of Internet/Web logic programming is based on the application of logic languages (Prolog and its modern descendants) that are very useful tools for representation, search and analysis of information because of their mathematical basis and ideology.
There are three main directions of using logic languages in the Internet applications:
- The first direction is the Internet programming in the logic languages. A lot of modern implementations of Prolog already have all means that are necessary for professional applied programming (see, for example, Visual Prolog [40]).
- The second direction is development of mobile Internet agents. There are special logic languages (see, for example, Jinni [37] and MINERVA [20]) that can implement the same functions as Java.
- The third one is the using the logic languages as a text format for representing information in the Internet [33]. This representation of information is suitable both for a person and for the intellectual agents.
However we suppose that the potential of logic is much more significant. We believe that the information processing in the Internet should be based on strict mathematical methods, and that the principles and means of logic object-oriented programming are very promising for developing these methods. Unfortunately, modern logic languages and tools for Internet programming do not provide strict declarative semantics of programs. In this paper we propose a new logical model and language to solve this problem.
In the first section of the paper we consider the advantages of logic languages in the context of Internet applications and modern approaches to Internet/Web logic programming. In the second one we describe the proposed model and language for logic object-oriented programming. In the third one we discuss the promises of application of developed means in the Internet/Web programming.
1. The advantages of logic programming
The field of Internet/Web logic programming has a rapid growth during the last five years [11,12,15,19,39]. The idea of using the logic languages and logic programming [5,35,9,10,34,1] in the Internet applications is based on the follows:
1. Logic languages have a powerful mathematical basis (a presence of declarative semantics). The declarative semantics provides a very high level of abstraction of the logic tools for representing and querying information.
2. The syntax of logic languages is more simple and powerful than one of the imperative languages because of (a) they are pointer-free, and (b) the operational semantics of these languages is based on the means of recursion and backtracking.
2.1. The data items of the logic languages (terms) are self-defined. So, any data item in Prolog has clear and unambiguous text representation.
2.2. The simplicity of syntax and operational semantics of logic languages are very promising for solving the problems of security and safety, because these problems can be solved with the help of automatic analyzing and transforming the logic programs.
3. The ideology of Prolog is based on the idea of search on the tree of possible solutions. This principle is very convenient for the search in the global Net.
4. Prolog is very suitable tool for natural language processing. So, it is very convenient for parsing and analyzing of HTML pages and so on.
These advantages are the basis of modern developments in the area of Internet/Web logic programming. Let us outline the main directions of research and development in this area, basically following [24]:
1. The first direction is development of methods and tools for logic programming the client-side systems. There are:
1.1. Special libraries for development of client-side systems (for example, ECLiPSe Prolog HTTP library [4], PiLLoW/CIAO [6], Visual Prolog [40], Win-Prolog [42]), the extensions of HTML with the Prolog-like syntax [33] and a lot of projects integrating Prolog with Java (Amzi!Prolog [2], JESS [17], Jinni [37], JIPL [21], jProlog [14], Kiev [22], MINERVA [20], NanoProlog [7], NetProlog [13], Visual Prolog [40], Win-Prolog [42], W-Prolog [41]).
1.2. Logical means and tools for search of information in the Internet (ADOOD [18], D3Web [25], LogicWeb [24], W-ACE [32], WebLog [23], WG-log [8]).
2. The second direction is development of tools for logic programming the server-side systems (ECLiPSe HTTP server library [4], EMRM Knowledge base [36], logical wrappers [3], ProWeb [42], Visual Prolog [40], WebLS [2]).
3. And the third one is the projects of developing logical methods and tools for coordinating the systems of intercommunicated agents in the Internet (Jinni [37], LogiMOO [38], Pamela [16], Visual Prolog [40], Win-Prolog [42]).
Thus, research and developments in the field of Internet/Web logic programming are very promising. However in despite of such activity in this field there is at least one mathematical problem that makes difficult to obtain the strict declarative semantics of Internet/Web logic programs.
There is a fundamental contradiction between the dynamic nature of the Internet and the static declarative semantics of the logic languages. So, the application of modern logic languages assumes that the information in the Internet is static. To process dynamic information correctly it is necessary to run the logic program from the beginning each time when user needs the results. This requires a lot of resources. Also the incorrect results will be obtained if the information changes during the program execution. We developed an approach to solve this problem.
2. An approach to provide the strict declarative semantics
We developed a generalized logical model of information systems (we call it as "the logical actor model") [27,28,30]. This model (see figure) describes an information system as a logical theorem divided into the "logical actors". The logical actors are some subgoals of the theorem (A1,...,AN), interacting through common variables (V1,...,VM). The proof of this theorem is carried out in an object-oriented search space consisting of separate worlds (W1,...,WK), the topology of which corresponds to the structure of the simulated system. For instance, the box A4 on the figure denotes an actor that has subgoals executing in the worlds W2 and W3.
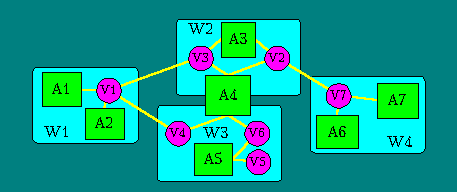
Fig. The logical actor model of information system.
The interaction between the logical actors is implemented with the help of the "correct destructive assignment" operation. The correctness means that this operation does not disturb the declarative semantics of the program. During this operation the necessary modifications of the values of common variables are carried out and then a repeated proof of actors depending on the old values of common variables is called. If the repeated proof of all these actors is finished with success, the execution of the operation also comes to the end with success; otherwise the usual backtracking of the logic program takes place.
The idea of repetitive proof of subgoals is the most interesting and important element of our model. This idea allows the correct (i.e. supporting declarative semantics) implementation of the destructive assignment in a logic language and thus is suitable for logical processing the information which may be changed during the processing.
We have developed the logic object-oriented language Actor Prolog [26,27,29] based on this model. This language implements structural and dynamical aspects [27] of the object-oriented approach.
The main features of this language are the follows:
- Actor Prolog is based on the classical first order logic. So, it is free of disadvantages of nonmonotonic logic systems.
- The main principle and the essence of the language are active revealing and eliminating of logical inconsistencies between the interacting objects.
- The ideology of the language allows implementing a visual (event-driven) user interface in correct way from the logical point of view.
3. Applications and promises
We successfully used these model and language to develop few experimental systems implementing visual modeling and programming tools. In particular, we designed the method and technique for logical description and analysis of functional (SADT) diagrams [27,30]. Our research showed the possibility and promising of the visual representation of applied information systems with the help of SADT diagrams animated by the means of logic object-oriented programming.
So, what are the advantages, that one can obtain using logical actor model and Actor Prolog in the Internet applications? Let us compare Actor Prolog with other modern logic languages.
The declarative semantics of "usual" Prolog guarantees the completeness and soundness of the search, and thus provides the mathematical strictness of the search process. However if the structure of the search space is changed during the search, the completeness and soundness of the "usual" Prolog are violated - so the search must be controlled manually to guarantee the correctness of the results of the search.
However in the case of Actor Prolog the control strategy of the language supports the completeness and soundness of the search during permanent changing of the search space. So, Actor Prolog can automate this important aspect of information processing in the Internet and provide the mathematical strictness of the search process in the conditions of changing information in the Internet.
We believe that the logical actor model and Actor Prolog will be useful in all three directions of Internet/Web logic programming mentioned in the Introduction.
Conclusion
We have discussed the advantages and problems of using logic programming for representation, search and analysis of information in the Internet. A generalized logical model of information systems and the main features of logic object-oriented language Actor Prolog based on this model were described. The control strategy of Actor Prolog supports the completeness and soundness of the search during changing information in the search space. This allows obtaining the strict declarative semantics of Internet/Web logic programs.
Bibliography
- Alexiev V. Mutable Object State for Object-Oriented Logic Programming: A Survey: Technical report TR93-15 / Dep. of Computing Science, University of Alberta. - Alberta, Canada, 1993. - 23 p. (ftp://ftp.cs.ualberta.ca/pub/oolog/state.ps.Z)
- Amzi!Prolog. WebLS - Embed Intelligent Components on Web Pages, 1999. (http://www.amzi.com)
- Bonnet Ph., Bressan S. Extraction and Integration of Data from Semi-structured Documents into Business Applications // Proc. of the 10th Symposium and Exhibition on Industrial Applications of Prolog. - Kobe, Japan, 1997. (http://context.mit.edu/~coin/publications/inap97/inap97.ps)
- Bonnet Ph., Bressan S., Leth L., Thomsen B. Towards ECLiPSe Agents on the Internet // Proc. of the 1st Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Bonn, Germany, 1996 - PP. 1-9.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/miscdocs/lp-internet/eclipse/ea.html) - Bowen J. P. Logic Programming. Oxford University Archive, 1999. (http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/archive/logic-prog.html)
- Cabeza D., Hermenegildo M., Varmaa S. The PiLLoW/CIAO Library for INTERNET/WWW Programming Using Computational Logic Systems // Proc. of the 1st Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Bonn, Germany, 1996 - PP. 43-62.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/miscdocs/lp-internet/pillow/lpnet3.html) - Calejo M., Sousa J. P. Embedding Prolog in the Java environment // Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Leuven, Belgium, 1997. - PP. 108-116. (http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/lpnet/proceedings97/calego/calego.html)
- Damiani E., Tanca L. WG-LOG: A Graph-Oriented Language for the World Wide Web // Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Leuven, Belgium, 1997. - PP. 129-148.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/lpnet/proceedings97/edamiani.ps) - Davison A. A Survey of Logic Programming-based Object-Oriented Languages // P. Wegner, A. Yonezawa, and G. Agha, editors, Research Directions in Concurrent Object Oriented Programming. - MIT Press, 1993. - PP. 42-106.
(http://www.cs.mu.oz.au/tr_db/mu_92_03.ps.gz) - Davison A. Logic Programming Languages for the Internet // A. Kakas, F. Sadri, editors, Computational Logic: From Logic Programming into the Future. - Springer Verlag, 2001. (http://fivedots.coe.psu.ac.th/%7Ead/papers/summBob.ps.gz)
- Davla J. (Web page author), editor. On-line Abstracts for "Logic Programming and the Internet, Opportunities and Challenges, A Compulog Net Workshop at Imperial College", December 1996. - London, U.K., 1996.
(http://www-lp.doc.ic.ac.uk/lp-internet/lp-int-abs.html) - de Bosschere K., Hermenegildo M., Tarau P., editors. Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications (in conjunction with the 14th Int. Conf. on Logic Programming), July 1997. - Leuven, Belgium, 1997. (http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/lpnet/proceedings97/proceedings.html)
- de Carvalho C. L NetProlog Home Page, 2001. (http://netprolog.pdc.dk)
- Demoen B., Tarau P. jProlog, 1999. (http://www.cs.kuleuven.ac.be/~bmd/PrologInJava/)
- Eliens A. (Web page author), editor. Proc. of the Workshop on Logic Programming and the Web at the 6th Int. World Wide Web Conf., Aril 1997. - Santa Clara, U.S.A., 1997. (http://www.cs.vu.nl/~eliens/WWW6/index.html)
- Eliens A., De Bra P., Treur J., Brazier F., van Vliet H. Position paper: Web Agent Support Programming // Proc. of the Workshop on Logic Programming and the Web at the 6th Int. World Wide Web Conf. - Santa Clara, U.S.A., 1997. (http://www.cs.vu.nl/~eliens/WWW6/papers/wasp/)
- Friedman-Hill E. J. JESS: The Java Expert System Shell (Version 5.0, alpha), July 1999. (http://herzberg.ca.sandia.gov/jess)
- Giannotti F., Manco G., Pedreschi D. A Deductive Data Model for Representing and Querying Semistructured Data // Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Leuven, Belgium, 1997. - PP. 55-67. (http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/lpnet/proceedings97/manco.ps)
- Giorgini P. (Web page author), editor. Proc. of the Joint one-day Workshop on the Future of Logic-based Agents, Imperial College, March 1999. - London, U.K, 1999. (http://www.cs.unitn.it/~pgiorgio/workshop/)
- IF Computer. MINERVA, 1999. (http://www.ifcomputer.com/MINERVA/)
- Kino N. JIPL, 1999 (http://www.kprolog.com/jipl/jipl_e.html)
- Kizub M. Kiev: Compiler which extends and unites the Java language and the Prolog language, 1999. (http://forestro.com/kiev/)
- Lakshmanan L. V. S., Sadri F., Subramanian I. N. A Declarative Approach to Querying and Restructuring the World-Wide-Web. Post-ICDE Workshop on Research Issues in Data Engineering (RIDE'96). - New Orleans, U.S.A., 1996. (ftp://ftp.cs.concordia.ca/pub/laks/papers/ride96.ps.gz)
- Loke S. W. Adding Logic Programming Behaviour to the World Wide Web: PhD Thesis. - Melbourne, Australia, 1998.
(http://www.cs.mu.oz.au/~swloke/logicweb-thesis.html) - Montes A. J. F., Del Valle Y. M. I. Querying the Web with Datalog: D3Web, 1998. (ftp://polaris.lcc.uma.es/~yague/iadt98_d3web.pdf)
- Morozov A. A. Actor Prolog // Programmirovanie. - 1994. - N 5. - PP. 66-78. - In Russian.
- Morozov A. A. Logical Analysis of Functional Diagrams during Interactive Designing of the Information Systems: The PhD Thesis. - Moscow, 1998. - 199 p. - In Russian. (http://www.cplire.ru/Lab144/auto.html)
- Morozov A. A., Obukhov Yu. V. A Logical Actor Model of Applied Open Systems // Development and Application of Open Systems: Proc. of the II Int. Conf. - Petrozavodsk, 1995. - PP. 28-30. - In Russian.
- Morozov A. A., Obukhov Yu. V. Actor Prolog. Programming Language Definition. - Moscow, 1996. - IRE RAS Preprint 2(613) of 14.06.96. - 57 p. - In Russian. (http://www.cplire.ru/Lab144/index.html)
- Morozov A. A., Obukhov Yu. V. Interactive Semantic Analysis of SADT Diagrams of the Information Systems by the Means of Object Oriented Logic Programming // Development and Application of Open Systems: Proc. of the IV Int. Conf. - Nizhny Novgorod, 1997. - PP. 61-64. - In Russian. (http://www.rapros97.nnov.ru/reports/9.html)
- Morozov A. A., Obukhov Yu. V., Olejnikov A. Ja. Logic Programming of Open Systems // Proc. of the XI Int. Conf. on Logic, Methodology and Philosophy of Science, v. II. - Moscow-Obninsk, 1995. - PP. 153-156. - In Russian. (http://www.cplire.ru/Lab144/obninsk.html)
- Pontelli E., Gupta G. W-ACE: A Logic Language for Intelligent Internet Programming // Proc. of the IEEE 9th Int. Conf. on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, 1997. - PP. 2-10.
- Price R. No More "Me Too" - Different approaches to Logic Documents // Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Leuven, Belgium, 1997. - PP. 28-40. (http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/lpnet/proceedings97/price.ps)
- Sadri F., Toni F. Computational Logic and Multiagent Systems: a Roadmap. - 1999. (http://citeseer.nj.nec.com/sadri99computational.html)
- Schneider M., Katz M. Object-Oriented Language: Prolog, 1999.
(http://cetus-links.org/oo_prolog.html) - Szeredi P., Molnar K., Scott R. Serving Multiple HTML Clients from a Prolog Application // Proc. of the 1st Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Bonn, Germany, 1996. - PP. 81-90.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/miscdocs/lp-internet/iqsoft/multiple.html) - Tarau P. Jinni [Java Inference Engine and Networked Interdictor] A Prolog Interpreter in Java for Mobile Agent Scripting and Internet Programming. - 1999. (http://www.binnetcorp.com/Jinni/index.html)
- Tarau P., De Bosschere K. Virtual World Brokerage with Bin-Prolog and Netscape // Proc. of the 1st Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications. - Bonn, Germany, 1996. - PP. 63-80.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/miscdocs/lp-internet/lpnet10/art.html) - Tarau P., Davison A., De Bosschere K., Hermenegildo M., editors. Proc. of the 1st Workshop on Logic Programming Tools for Internet Applications (in conjunction with the Joint Int. Conf. and Symposium on Logic Programming), September 1996. - Bonn, Germany, 1996.
(http://www.clip.dia.fi.upm.es/miscdocs/lp-internet/archive.html) - Visual Prolog. - Prolog Development Centre, 1999. (http://www.pdc.dk)
- Winikoff M. W-Prolog 1.2, 1999. (http://members.xoom.com/winikoff/wp/)
- Win-Prolog. - LPA, 1999. (http://www.lpa.co.uk)